Ecological dynamics
As ecological condition declines, silver buffaloberry, willow, rose, big sagebrush, black greasewood, and rubber rabbitbrush increase and become the dominant vegetation in lower condition classes. Inland saltgrass increases as conditions decline and usually dominates the understory. Fivehook bassia and annual mustards are species likely to invade this site.
Fire Ecology:
Grassland communities with a basin wildrye component historically experienced mostly infrequent to frequent stand replacing fires. Grassland vegetation types experienced both short fire intervals of less than 35 years as well as intervals ranging from 35 to 100 years, depending on climate and ignition sources. Basin wildrye is top-killed by fire. Older basin wildrye plants with large proportions of dead material within the perennial crown can be expected to show higher mortality due to fire than younger plants having little debris. Basin wildrye is generally tolerant of fire but may be damaged by early season fire combined with dry soil conditions. Alkali sacaton is classified as tolerant of, but not resistant to, fire. Top-killing by fire is probably frequent, and the plants can be killed by severe fire. Alkali cordgrass has high fire tolerance. Alkali cordgrass grows in areas that do not burn regularly due to the high moisture content of the plant community. Saltgrass rhizomes occur deep in the soil where they are insulated from the heat of most fires. Saltgrass survives fire by sending up new growth from rhizomes. Silver buffaloberry is probably killed by severe fires. Silver buffaloberry has fair tolerance to fire in the dormant state and sprouts from rootstocks following fire. Basin big sagebrush is readily killed when aboveground plant parts are charred by fire. Prolific seed production from nearby unburned plants coupled with high germination rates enables seedlings to establish rapidly following fire.
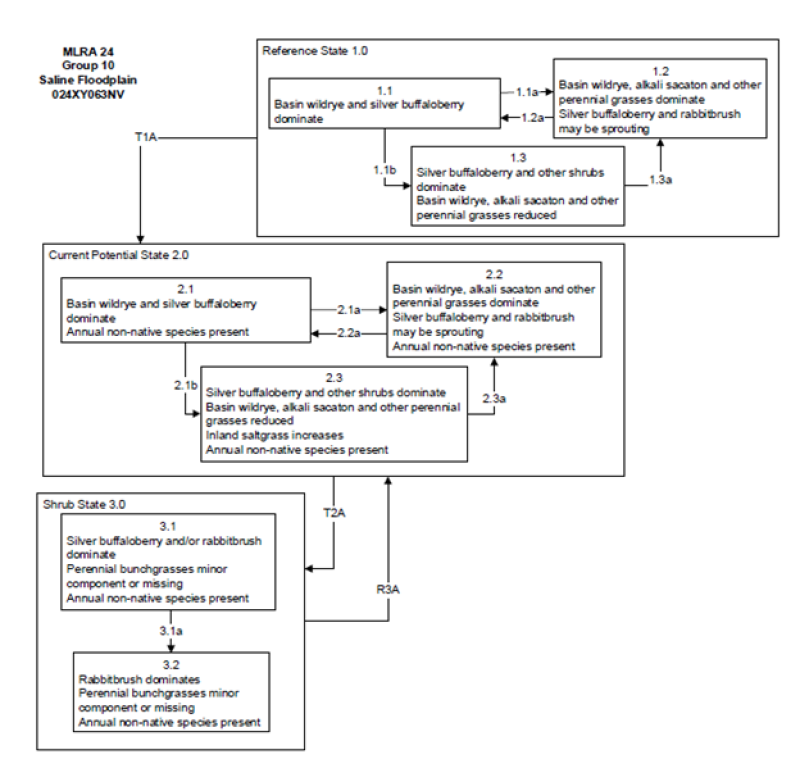
State 1
Reference State
The Reference State 1.0 is a representative of the natural range of variability under pristine conditions. The Reference State has three general community phases: a shrub-grass dominant phase, a perennial grass dominant phase and a shrub dominant phase. State dynamics are maintained by interactions between climatic patterns and disturbance regimes. Negative feedbacks enhance ecosystem resilience and contribute to the stability of the state. These include the presence of all structural and functional groups, low fine fuel loads, and retention of organic matter and nutrients. Plant community phase changes are primarily driven by fire, periodic drought and/or insect or disease attack.
Community 1.1
Reference Plant Community
The reference plant community is dominated by silver buffaloberry, basin big sagebrush, basin wildrye, and alkali sacaton. This site is characterized by medium to dense thickets of silver buffaloberry with lesser amounts of willow, rose and sumac. Understory vegetation occurs within interspaces of thickets and at dripline along thicket edge.
Potential vegetative composition is about 55% grasses, 5% forbs and 40% shrubs.
Approximate ground cover (basal and crown) is 25 to 40 percent.
Table 5. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type |
Low
(lb/acre) |
Representative value
(lb/acre) |
High
(lb/acre) |
| Grass/Grasslike |
495 |
770 |
990 |
| Shrub/Vine |
360 |
560 |
720 |
| Forb |
45 |
70 |
90 |
| Total |
900 |
1400 |
1800 |
Community 1.2
Reference Community 1.2
This community phase is characteristic of a post-disturbance, early-seral community phase. Basin wildrye and alkali sacaton dominate the community. Black greasewood will decrease but will likely sprout and return to pre-burn levels within a few years. Early colonizers such as rabbitbrush and shadscale may increase.
Community 1.3
Reference Community 1.3
Black greasewood and big sagebrush increase in the absence of disturbance. Decadent shrubs dominate the overstory and deep-rooted perennial bunchgrasses in the understory are reduced either from competition with shrubs, herbivory, drought or combinations of these.
Pathway 1.1a
Community 1.1 to 1.2
Fire will decrease or eliminate the overstory of black greasewood and allow the perennial bunchgrasses to dominate the site. Fires will typically be low severity, resulting in a mosaic pattern due to low fuel loads. A fire following an unusually wet spring may be more severe and reduce sagebrush cover to trace amounts.
Pathway 1.1b
Community 1.1 to 1.3
Absence of disturbance over time, significant herbivory, long term drought or combinations of these would allow the black greasewood overstory to dominate the site and reduce the perennial bunchgrasses. Inland saltgrass may increase in the understory depending on the timing and intensity of herbivory. Heavy spring utilization will favor an increase in black greasewood.
Pathway 1.2a
Community 1.2 to 1.1
Time and lack of disturbance will allow shrubs to increase.
Pathway 1.3a
Community 1.3 to 1.2
Fire will decrease the overstory of black greasewood and allow the perennial bunchgrasses to dominate the site. Fires will typically by high intensity in this phase due to the dominance of black greasewood resulting in removal of the overstory shrub community.
State 2
Current Potential State
This state is similar to the Reference State 1.0 with three similar community phases. Ecological function has not changed, however the resiliency of the state has been reduced by the presence of invasive weeds. Non-natives may increase in abundance but will not become dominant within this State. These non-natives can be highly flammable and can promote fire where historically fire had been infrequent. Negative feedbacks enhance ecosystem resilience and contribute to the stability of the state. These feedbacks include the presence of all structural and functional groups, low fine fuel loads, and retention of organic matter and nutrients. Positive feedbacks decrease ecosystem resilience and stability of the state. These include the non-natives’ high seed output, persistent seed bank, rapid growth rate, ability to cross pollinate, and adaptations for seed dispersal.
Community 2.1
Community Phase 2.1
This community is dominated by basin wildrye and black greasewood. Alkali sacaton and rabbitbrush are also common on these sites. Inland saltgrass, alkaligrass and other perennial bunchgrasses and shrubs make up smaller components. Non-native annual species such as halogeton and cheatgrass are present.
Community 2.2
Community Phase 2.2
This community phase is characteristic of a post-disturbance, early-seral community phase. Basin wildrye and alkali sacaton dominate the community. Black greasewood will decrease but will likely sprout and return to pre-burn levels within a few years. Early colonizers such as rabbitbrush and shadscale may increase. Annual non-native species are stable to increasing in the community.
Community 2.3
Community Phase 2.3
Black greasewood and big sagebrush increase in the absence of disturbance. Decadent shrubs dominate the overstory and deep-rooted perennial bunchgrasses in the understory are reduced either from competition with shrubs, inappropriate grazing management, drought or combinations of these.
Pathway 2.1a
Community 2.1 to 2.2
A low severity fire would decrease the overstory of black greasewood and allow the understory perennial grasses to increase. Fires are typically low severity resulting in a mosaic pattern due to low fuel loads. A fire following an unusually wet spring facilitating an increase in fine fuels may be more severe and reduce black greasewood cover to trace amounts. Brush treatments would also reduce the shrub overstory and allow the perennial grasses in the understory to increase.
Pathway 2.1b
Community 2.1 to 2.3
Absence of disturbance over time, inappropriate grazing management, long term drought, lowering of the water table by groundwater pumping or channel incision or combinations of these would allow the black greasewood overstory to dominate the site and reduce perennial bunchgrasses. Inland saltgrass may increase in the understory depending on the timing and intensity of grazing. Heavy spring utilization will favor an increase in black greasewood.
Pathway 2.2a
Community 2.2 to 2.1
Time and lack of disturbance will allow shrubs to increase, this may be coupled with inappropriate grazing management.
Pathway 2.3a
Community 2.3 to 2.2
Release from drought and/or water table recovery would allow an increase in perennial bunchgrasses. Fire and/or brush treatments will also decrease the overstory of black greasewood and give a competitive advantage for existing perennial
State 3
Shrub State
This state has two community phases, one that is characterized by a co-dominance of black greasewood and rabbitbrush and the other with rabbitbrush overstory. This site has crossed a biotic threshold and site processes are being controlled by shrubs. Bare ground has increased and pedestalling of grasses may be excessive.
Community 3.1
Community Phase 3.1
Decadent black greasewood dominates the site. Perennial bunchgrasses are present but a minor component. Annual non-native species may be present and may be increasing in the understory.
Community 3.2
Community Phase 3.2
Rabbitbrush dominates the overstory. Deep-rooted perennial bunchgrasses may be present in trace amounts or absent from the community. Annual non-native species increase. Bare ground is significant.
Pathway 3.1a
Community 3.1 to 3.2
Soil disturbing treatments such as plowing and drill seeding would decrease black greasewood and allow rabbitbrush to dominate site. Lowering of the water table through groundwater pumping and/or channel incision would also decrease black greasewood.
Transition T1A
State 1 to 2
Trigger: This transition is caused by the introduction of non-native annual plants, such as cheatgrass, mustards, halogeton and Russian thistle.
Slow variables: Over time the annual non-native species will increase within the community.
Threshold: Any amount of introduced non-native species causes an immediate decrease in the resilience of the site. Annual non-native species cannot be easily removed from the system and have the potential to significantly alter disturbance regimes from their historic range of variation.
Transition T2A
State 2 to 3
Trigger: To Community Phase 3.1 or 3.2: Inappropriate cattle/horse grazing will decrease or eliminate deep rooted perennial bunchgrasses and favor shrub growth and establishment. To Community Phase 3.2: Severe fire will reduce and/or eliminate black greasewood and decrease perennial bunchgrasses. Lowering of the water table through groundwater pumping and/or channel incision will initially cause an increase in shrubs, however as the water table decreases further black greasewood will be reduced. Soil disturbing brush treatments will reduce greasewood and possibly increase non-native annual species.
Slow variables: Long-term decrease in deep-rooted perennial grass density and/or black greasewood.
Threshold: Loss of deep-rooted perennial bunchgrasses changes nutrient cycling, nutrient redistribution, and reduces soil organic matter. Loss of long-lived, black greasewood changes the temporal and depending on the replacement shrub, the spatial distribution of nutrient cycling.
Restoration pathway R3A
State 3 to 2
Restoration of this state would require mechanical or chemical brush treatment and control of weedy annual species. Restoration may also require an increase in the water table, including repair of incised channel(s) and/or reduced groundwater pumping. Seeding of grasses may be necessary if basin wildrye is severely reduced or no longer present in the community. Fire is not a recommended treatment.